Wide social influence and the emergence of the unexpected: An empirical test using Spotify data
Sociological Science (2025)
Identifies theoretical conditions under which social influence generates unexpected collective outcomes.

Sociological Science (2025)
Identifies theoretical conditions under which social influence generates unexpected collective outcomes.
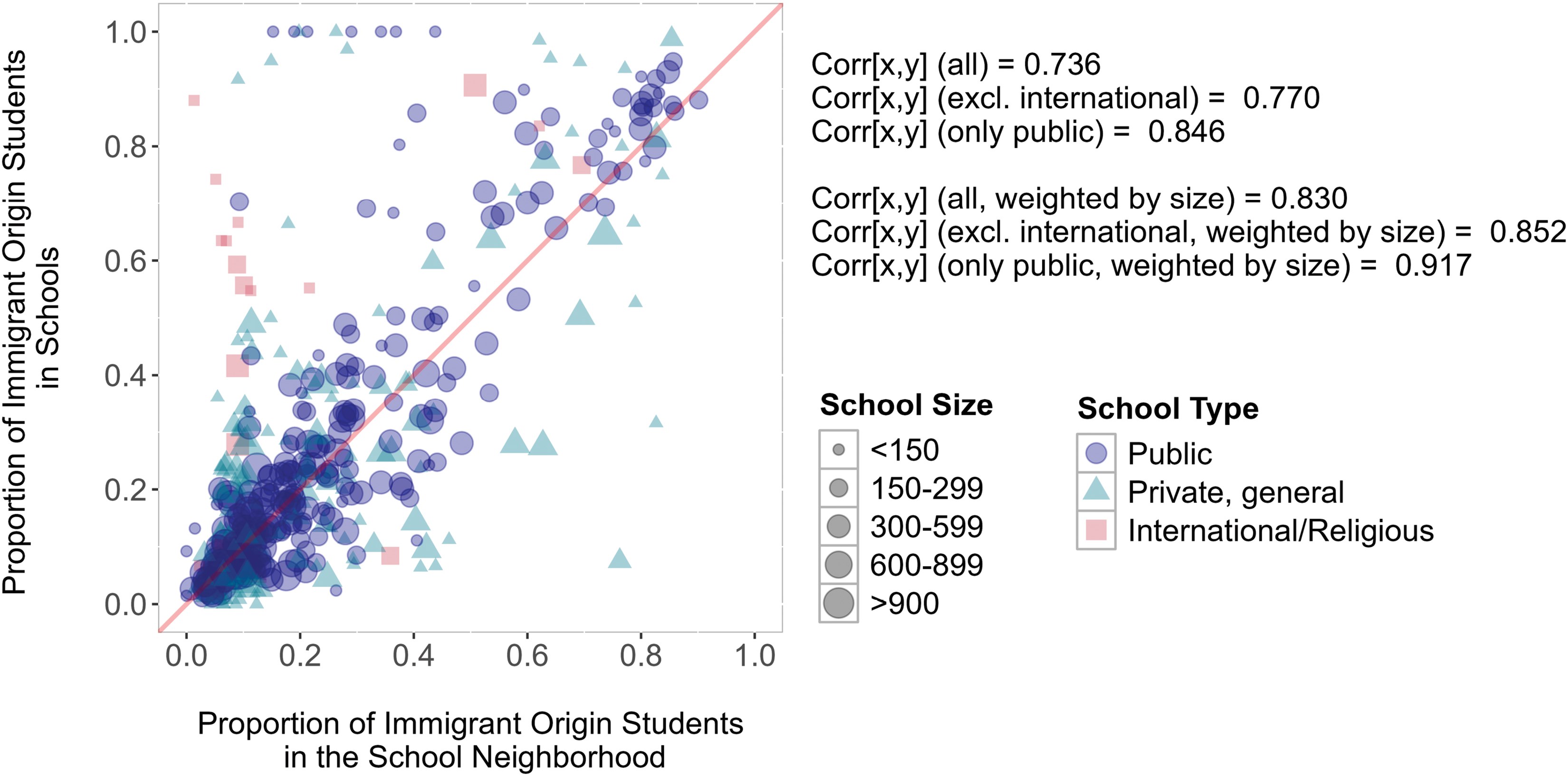
European Sociological Review (2025)
Shows that ethnicity-related school preferences have relatively little impact on ethnic segregation because the schools that students choose among tend to have similar ethnic compositions.

Handbook of Computational Social Science (2025)
Proposes a way for bridging the explanatory principles of analytical sociology with the research designs of computational social science.

The Oxford Handbook of the Sociology of Machine Learning (2024)
Reviews strategies for estimating social influence influence effects using modern, large-scale data together with machine learning.
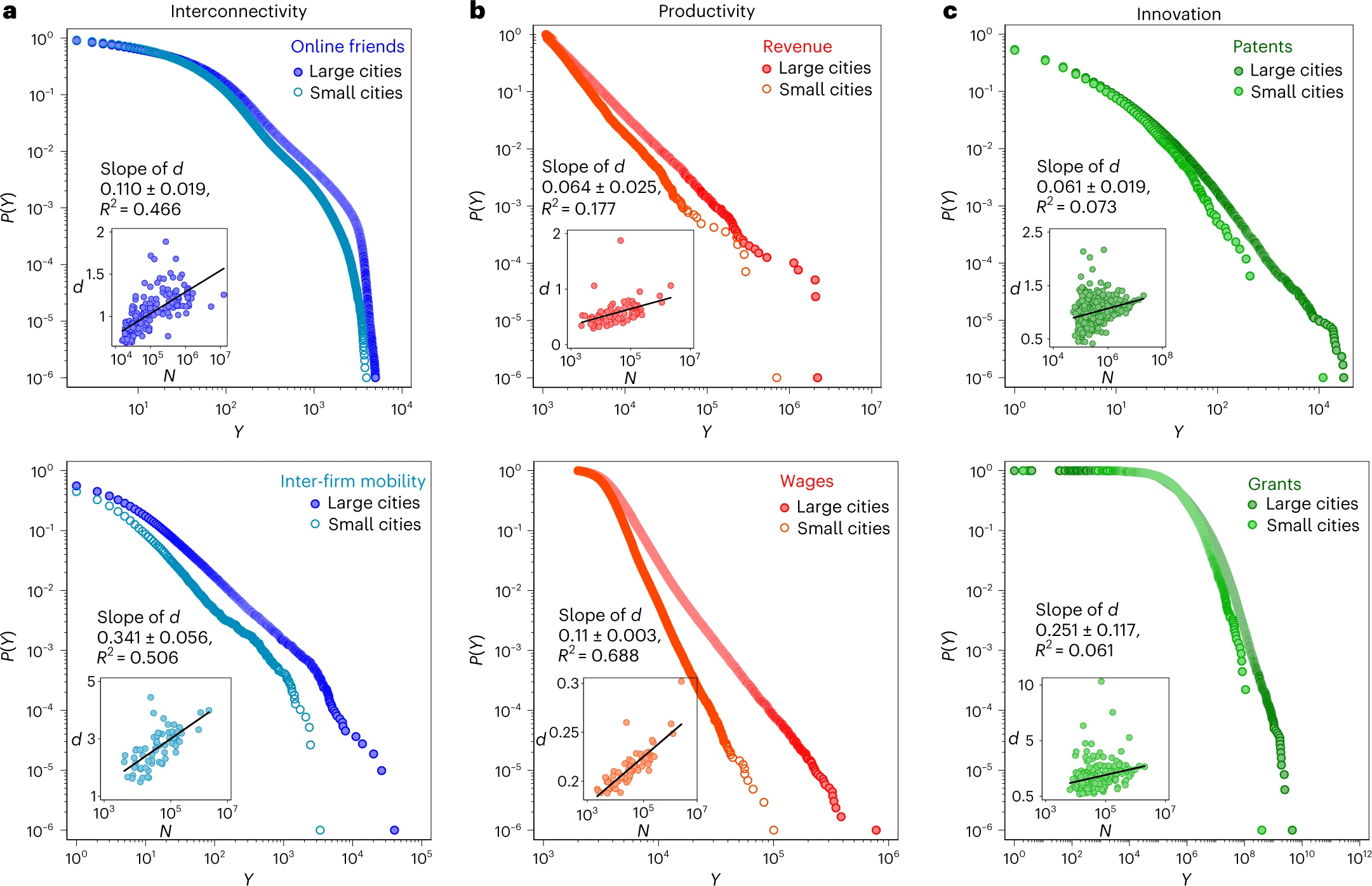
Nature Human Behaviour (2023)
Shows that a large fraction of observed between-city inequalities can be explained by the distributional 'tails' of large cities. Identifies a cumulative advantage mechanism that reproduces the key patterns.
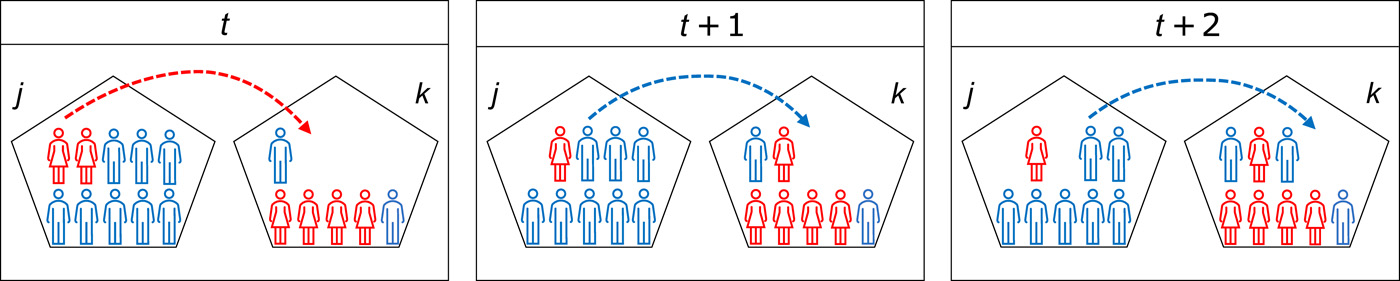
Science Advances (2021)
Identifies a mechanism which shows how network mobility sometimes can have desegregating effects.

EMNLP (2019)
Proposes a new method, using informative Bayesian priors, for creating domain-informed, interpretable word embedding dimensions.